

Once in a while, a bone is put under more stress than it can handle.
/GettyImages-480791953-56b679535f9b5829f832e6ea.jpg)
They are strong and flexible enough to absorb the light impact your body experiences during these activities.
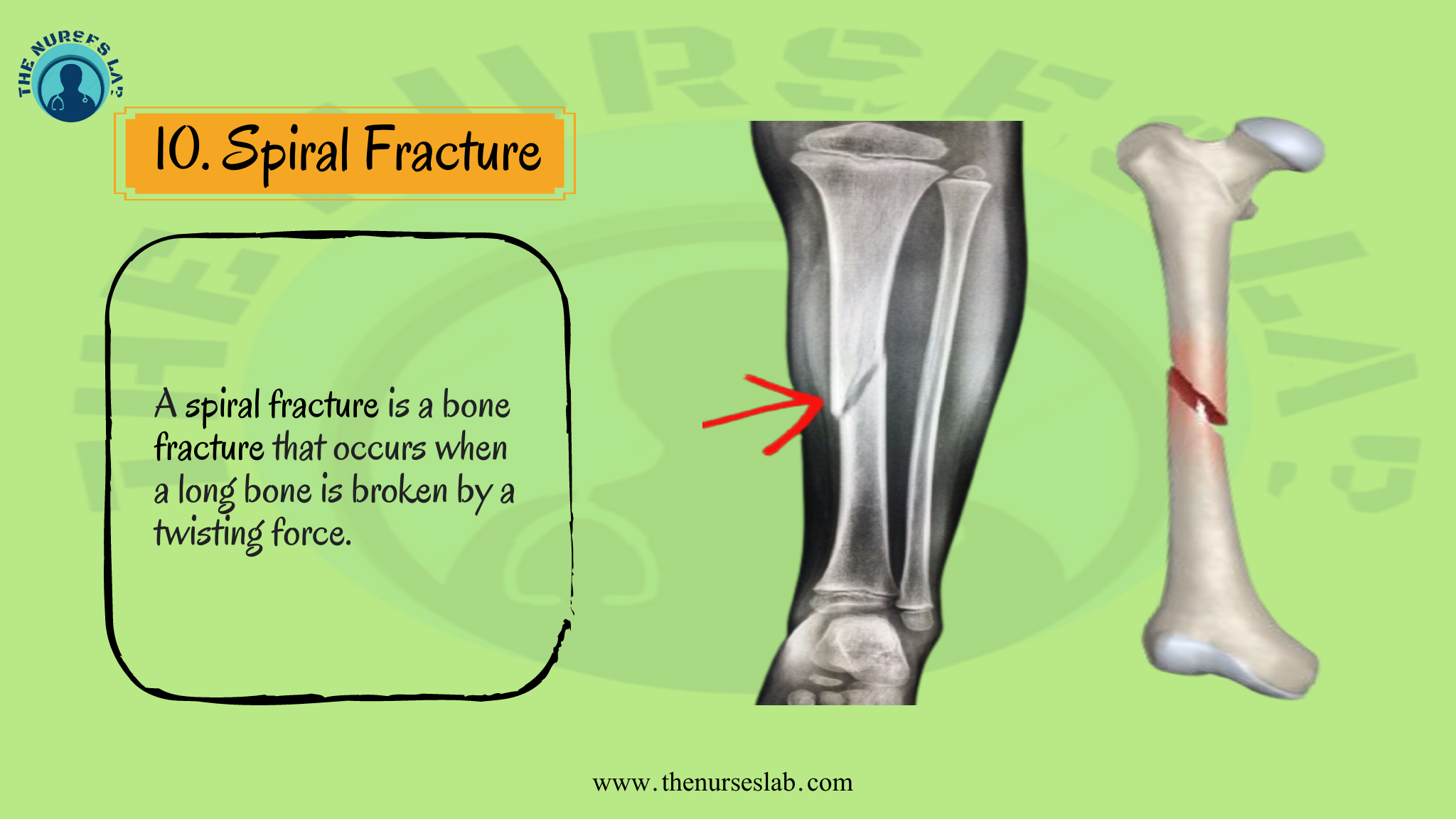
When you break a bone, you get increased bone turnover and associated inflammatory factors and I suspect that in underlying diseases, this process is not well controlled and a fracture may fuel underlying health issues," she said.Bones usually have no problem supporting your body as you go about your daily activities, including exercise and play. The researchers said it is not yet understood why there is a connection between multiple underlying health conditions, the type of fracture and poor outcomes.īut the interaction between bones and the immune system may be key, professor Jacqueline Center, the study's lead author and head of the Garvan Institute's clinical studies and epidemiology laboratory, said in the release. Other clusters were similarly sorted by severity of illness. They noted, for example, that many patients with a history of prior cancers were not in the cancer cluster, but this cluster included virtually all patients who showed evidence of advanced cancer. The scientists took into account the severity of the study participants' chronic illnesses and their combinations: clusters distinguished individuals with advanced, complex or late-stage disease from those with earlier-stage disease. Overall, 43% of patients with fractures had at least two illnesses, or comorbidities.
In one example of differences, the researchers said men with a forearm fracture in the diabetic cluster had one-year excess mortality of 3.21 in the cardiovascular cluster, 5.44% in the hepatic and/or inflammatory cluster, 5.89% and in the cancer cluster, 7.59%. There was also a diabetic group and a cancer group, with an additional liver/inflammatory illness group for men only. In this group, the highest excess mortality was found in patients 1 year after hip fracture: 19.89% in men and 11.17% in women.Īlmost one-quarter of the study's participants with fractures were grouped in the cardiovascular cluster, in which most men and women had three or more comorbidities. The researchers found chronic health conditions at the time of fracture were naturally clustered into five specific groups for men and four for women: most fell in a relatively healthier group with generally only one or no health conditions, comprising 60.5% of men and 66.5% of women. The participants were followed at least two years post-fracture most follow-up ran 6 years, during which time 43% of men and 38.5% of women in the study died. RELATED Hip fracture recovery strongly linked to age, study saysįace, skull, finger or toe fractures and high-trauma fractures due to traffic accidents were excluded, the research paper said. Thach Tran, the study's corresponding author and research officer in the Skeletal Diseases Program at Garvan Institute of Medical Research in Sydney, Australia, said in the release. "This research highlights that there's an interaction between the fracture and a patient's cluster of health conditions - their underlying health - and that this could be a good way to identify at-risk people," Dr. They also found that study participants with underlying health conditions who had fractures closer to the body's center, such as in the hip, spine, upper arm or leg, had a higher mortality rate than what's expected for the general population of the same age, a news release said.Īccording to the researchers, the findings highlight the need to prevent fracture in high-risk patients and could change the way in which medical care is provided to older adults - promoting a new way of thinking about patients with fractures that considers the site of the broken bone in light of specific underlying health conditions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
